If you’ve been experiencing persistent neck and shoulder pain, Trapezitis might be the hidden culprit. This condition affects thousands of people but often goes undiagnosed. In this guide, you’ll learn about Trapezitis, its causes, common symptoms, and how to treat and prevent it effectively.
What is Trapezitis?
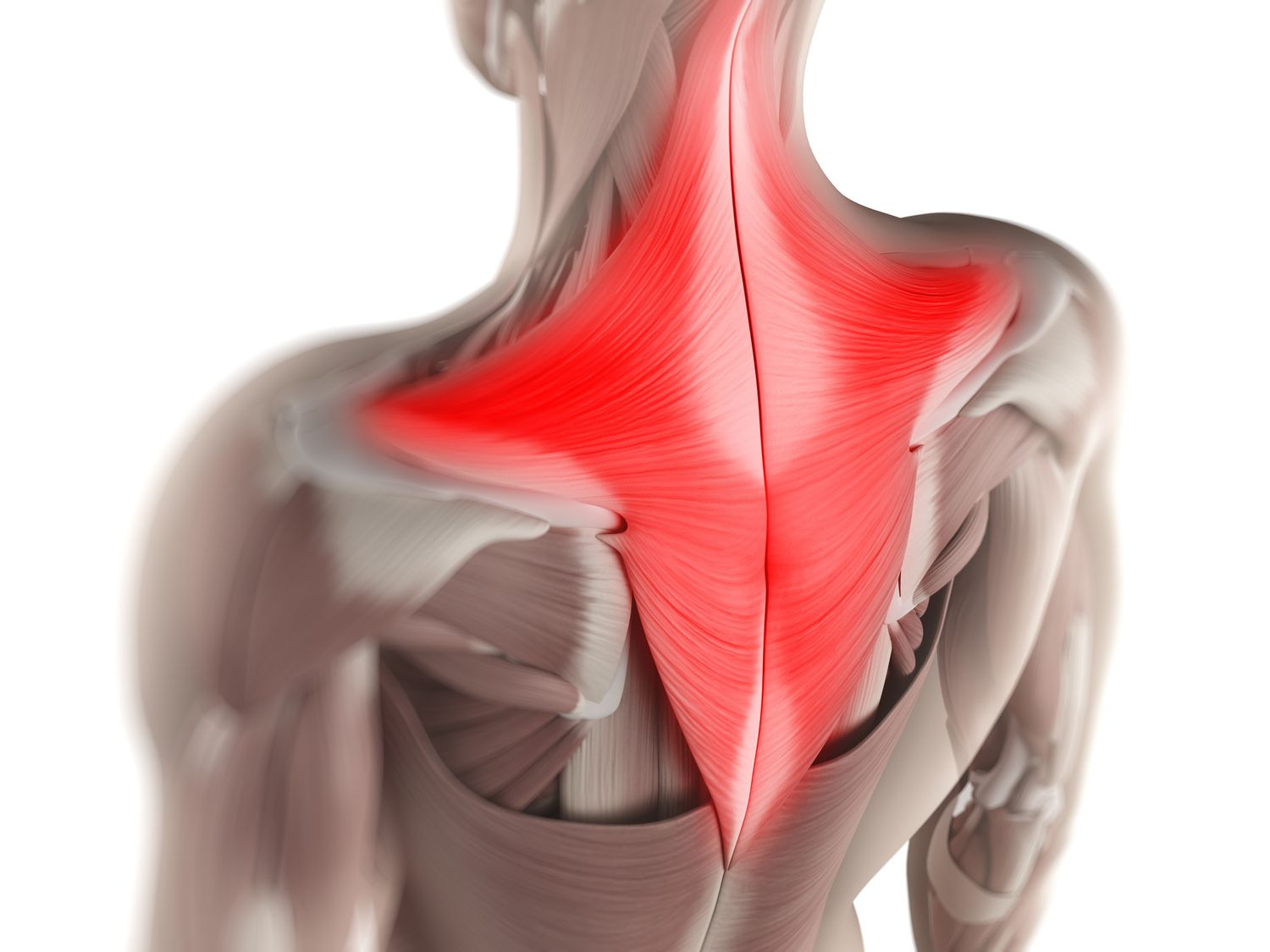
Trapezitis is the inflammation of the trapezius muscle, which is a large, triangular-shaped muscle extending from the back of your neck down to the shoulders and upper back. The trapezius plays a vital role in moving, rotating, and stabilizing your shoulder blades and extending your neck.
When this muscle becomes inflamed due to overuse, bad posture, or stress, it results in pain, stiffness, and discomfort—this condition is what we call Trapezitis.
Causes of Trapezius Muscle Strain:
- Poor Posture: One of the primary contributors to trapezius muscle strain is poor posture. Prolonged periods of sitting or standing with improper posture can lead to muscle imbalances and overuse of the trapezius muscle. Individuals who spend long hours working at a desk or using electronic devices are particularly prone to this issue.
- Overuse or Repetitive Movements: Engaging in repetitive movements or activities that strain the trapezius muscle can lead to overuse and subsequent strain. This is common in occupations that involve repetitive motions, such as lifting, carrying heavy objects, or performing overhead activities without proper rest and recovery.
- Muscle Tension and Stress: Emotional stress and tension can manifest physically, leading to increased muscle tension throughout the body, including the trapezius muscle. Chronic stress can contribute to the development of muscle knots and trigger points, causing discomfort and pain.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the supporting muscles around the trapezius, such as the neck and shoulder muscles, can place additional strain on the trapezius itself. A lack of strength and flexibility in these surrounding muscles may contribute to an increased risk of trapezius muscle strain.
- Injury or Trauma: Direct injury or trauma to the trapezius muscle, such as a fall or sudden impact, can result in muscle strain. This can happen in sports-related activities or accidents where the muscle is forced into an unnatural position.
Symptoms of Trapezitis
Recognizing Trapezitis early can help prevent it from becoming chronic. Common signs include:
- Persistent pain or stiffness in the neck and shoulders
- Tenderness in the trapezius area
- Headaches originating from neck tension
- Restricted shoulder and neck movement
- Muscle spasms or knots in the upper back
If you experience these symptoms frequently, consult a doctor or physiotherapist for proper diagnosis.
How to Treat Trapezitis
The good news is that Trapezitis can often be managed with simple lifestyle changes and treatments. Here are some effective options:
✅ Rest and posture correction: Take breaks from activities that strain the trapezius and maintain good posture.
✅ Apply heat or cold: Use a warm compress or ice pack on the affected area to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
✅ Pain relief medication: Over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen may help, but always consult a healthcare professional first.
✅ Stretching and exercises: Gentle neck and shoulder stretches strengthen the trapezius muscle and prevent stiffness.
✅ Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can recommend tailored exercises and techniques to reduce inflammation and restore mobility.
✅ Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to ease muscle tension.
Prevention Tips for Trapezitis
Preventing Trapezitis is all about reducing strain on the trapezius muscle. Here are some practical tips:
- Maintain a proper ergonomic setup at work.
- Avoid carrying heavy bags on one shoulder.
- Take short breaks to stretch when working long hours.
- Practice stress-relieving activities regularly.
- Strengthen shoulder and neck muscles through light exercise.
When to See a Doctor
While mild Trapezitis often improves with self-care, severe or persistent pain should not be ignored. If you notice worsening symptoms, weakness in your arms, or numbness, seek medical advice immediately.
Conclusion
Trapezitis can be a real pain in the neck—literally! Understanding how the trapezius muscle works and how inflammation occurs can help you tackle this condition effectively. With proper care, healthy habits, and timely treatment, you can keep Trapezitis at bay and enjoy pain-free movement once again.
Have questions about Trapezitis or your trapezius muscle health? Drop them in the comments below!